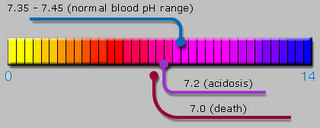
 The term pH, which means "potential hydrogen," represents a scale for the relative acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Acidity is measured as a pH of 0.1 to 6.9 and alkalinity as a pH of 7.1 to 14; a pH of 7.0 is considered neutral. The numbers refer to how many hydrogen atoms are present compared to an ideal or standard solution. Normally, blood is slightly alkaline, at 7.35 to 7.45; urine pH can range from 4.8 to 7.5, although normal is closer to 7.0.
The term pH, which means "potential hydrogen," represents a scale for the relative acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Acidity is measured as a pH of 0.1 to 6.9 and alkalinity as a pH of 7.1 to 14; a pH of 7.0 is considered neutral. The numbers refer to how many hydrogen atoms are present compared to an ideal or standard solution. Normally, blood is slightly alkaline, at 7.35 to 7.45; urine pH can range from 4.8 to 7.5, although normal is closer to 7.0.Acid-base metabolism refers to the metabolic processes that maintain the balance of acids and bases (alkalines) in body fluids. Acids release hydrogen ions, while bases accept them. The total number of these hydrogen ions present determines the pH of a fluid. Too many hydrogen ions (a pH below 7.0) produce an acidic state called acidosis; too few hydrogen ions (a pH above 7.0) cause an alkaline excess called alkalosis; both can lead to illness.
Oxidation-reduction is the basic chemical mechanism in the cell by which energy is produced from foods. Electrons (negatively charged particles in an atom) are removed from one atom, resulting in "oxidation" of this first atom, and then are added or transferred to another atom, resulting in "reduction" of this second atom. This continual process of energy metabolism is actually a flow of electrons, or a minute electrical current, within the cell.
Starter Cleansing Kit$96.90  Our Starter Cleansing Kit contains Super Phos 30, Paratrex™, and Oxy-Powder. |
No comments:
Post a Comment